SIX SIGMAS
Six Sigma is a management strategy that uses five stages: Define, Measure, Analyze, Improve, and Control. Six Sigma requires a consistent project concept. The primary goal of Six Sigma is to prevent problems before they occur.
BACK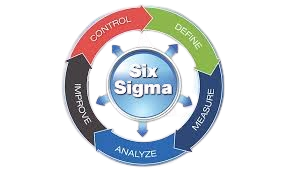
ADVANTAGES
- Increased Customer Satisfication
- Cost Reduction
- Sustainable Improvement
DISADVANTAGES
- Time Intensive
- Complex Methodology
- Resistance to Change
EXAMPLE
Microsoft uses Six Sigma to reduce system and data center defects and minimize IT infrastructure failures. It begins by setting standard benchmarks for hardware and software, then uses root-cause analysis and incident data to identify problem areas.
By prioritizing defects based on business impact and analyzing server data regularly, Microsoft was able to target and fix specific issues. This led to server availability, higher productivity, and greater customer satisfaction improvements.